Building more innovative operations that enable higher productivity and profitable output is vital to succeeding in the manufacturing sector. No wonder businesses have turned to the Internet of Things (IoT) to innovate their warehouses and ensure quick delivery of products. The modern arrangement has given birth to a critical terminology in the sector.
Smart Manufacturing
It is the process of using IoT technology in manufacturing processes for optimum efficiency. Smart Manufacturing aims to identify opportunities to use data analytics to improve manufacturing performance. It holds a special place in the Industrial IoT ecosystem.
Deployments involve embedding sensors in machinery to gather data on their operational status and improving security on your production floor.
Other technologies such as cyber-physical systems, fabrication technologies (3D printing), and quantum computing have accelerated the progress of Industry 4.0. There is another term that is heavily reliant on Smart Manufacturing; it is called Smart Factory.
Smart Factory
It is an automated production environment that continuously collates and shares data through connected devices, sensors, servers, equipment, and production systems.
A Smart Factory is a highly digitized shop floor where physical production is combined with smart computing, big data, and digital technology to create a more opportunistic system for businesses focusing on Supply Chain Management (SCM) and manufacturing.
Smart Manufacturing and the IoT driving industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is the ongoing automation of traditional manufacturing and the evolution of industrial practices using smart technology. When one thinks of “Industry 4.0,” it is hard not to think of it as a suite of technologies. In reality, that is what Industry 4.0 is!
The new phase in the Industrial Revolution focuses mainly on interconnectivity, real-time data, machine learning, and automation. It is also characterized by the integration of autonomous robots and machines with physical productions to create better-connected ecosystems.
Thanks to Industry 4.0, manufacturers have better control and visibility across their supply chains. They can predict problems before they arise — for instance, shutting down machinery before it shuts down. Manufacturers can also keep an eye on disposals, adjustments, asset transfers, and reclassifications.
How is Smart Manufacturing related to the IoT?
Smart Manufacturing enables factory managers to collect and analyze data for better decision-making and accordingly optimizing production. The data from sensors and equipment is communicated through IoT apps deployed at the factory level.
IoT technology enables data transmission from one end to another and manages processes remotely, changing production plans in real-time as and when needed.
Because connected smart products can feed information back to the factory, quality issues can be detected faster, and the product design can be adjusted early on. This dramatically improves the outcomes, reduces production waste, and yields high-quality products.
IoT enables manufacturers to optimize manufacturing processes related to cost, resource management, and performance. It is also great for collecting vendor or customer feedback.
Smart devices can offer insights into how consumers use them. In other words, there would be no Smart Manufacturing without IoT.
Location awareness in smart factories
Location tracking has been in use for a lot longer than one may guess. For instance, military organizations have been using trackers for decades. In police governance, tracking collars and ankle bracelets are widely used to ensure high-risk defendants do not flee the state.
Fast forward to 2021, and we are now looking at building Bluetooth-enabled refrigerators that can sense when milk is running low and determine whether the owner is passing a convenience store and alerting them accordingly.
Location awareness technology can also tell a person where the nearest hospital is if their wearable medical sensor detects the onset of a severe condition.
In manufacturing specifically, autonomous navigation becomes possible by equipping drones with asset tracking tags. Plus, digitized maps in warehouses combine asset tracking, wayfinding, and defined geofences capabilities under a single roof.
That way, the employees would not have any problem locating certain assets in the warehouses. This would save time and boost their efficiency.
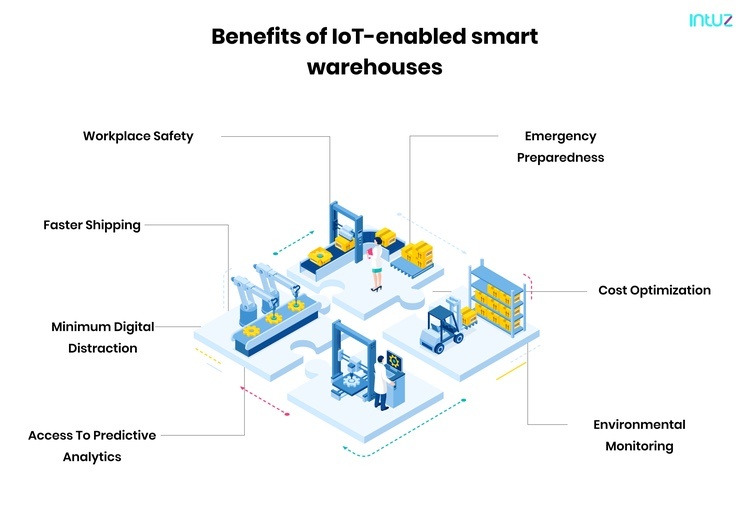
Benefits of IoT-enabled smart warehouses
1. Workplace safety
You will agree that manual handling of products involves ergonomic risks such as injuries to joints, nerves, tendons, and muscles caused by repetitive and strenuous motions (e.g., bending, heavy lifting, twisting).
Considering these risks, it makes sense to deploy automated machines that reduce human intervention, improve throughput and offer seamless visibility into bottlenecks. This not only eliminates data redundancy and human errors but also ensures worker safety.
2. Faster shipping
In traditional warehouses, order processing takes time because the workers have to manually locate the products, pick them up and fill orders. Besides, human error can cause delays in processing, sorting, and packing orders.
Smart warehouse solutions deploy collaborative mobile bots to eliminate the time taken to locate a product and the long walk taken by the workers to the designated aisles.
3. Minimum digital distraction
Smart warehouses leverage analytics tools, enterprise software, and machine learning algorithms to constantly identify suboptimal operational components and workflows, providing insights that inform improvements in a streamlined fashion.
That way, warehouse operators can remove any digital distractions and focus solely on monitoring key performance indicators to make data-driven decisions.
4. Access to predictive analytics
Using advanced analytics to fetch insights into the orders processed by the warehouse is on the rise. Predictive analysis helps you estimate future orders, planning for spikes or reductions in demand, and optimizing warehouse operations. Automated picking bots and employees are better aligned with predictive models, which result in faster order processing and shipping.
5. Emergency preparedness
Smart technologies help warehouses be better prepared for any emergency. Using sensors, videos, network recovery solutions, and cyber-physical systems, you can be alerted if something is about to go down in the warehouse — for instance, a fire or a power outage.
6. Cost optimization
The average wages in the manufacturing sector have been on the rise for more than a decade. In fact, labor costs consist of nearly two-thirds of warehouse operating expenses.
Smart warehouses reduce the demand for labor by deploying automated bots and leveraging Sensing as a Service to pick up tasks on their behalf. This reduces not only human error in order handling and processing but also saves high labor costs.
7. Environmental monitoring
If you are into food manufacturing, you will agree on how important it is to ensure the product remains fresh and of high quality. IoT sensors help track the moisture content in the items produced, effectively saving you a lot of money.
The amount of water a product has can affect its appearance, taste, stability, and shelf life. Since you strive to sell the best-finished product, IoT helps you take action on those faltering products, thus ensuring less wastage.
Security — a concern in smart manufacturing
IoT technology is valuable in achieving higher productivity levels, faster remediation of quality defects, superior collaboration across multiple functions. But when two or more devices, sensors, and servers are connected, the arrangement multiplies security vulnerabilities for that particular network. The Smart Factory is no exception.
Many manufacturing businesses are witnessing an increase in cybercrimes associated with the control systems used for managing industrial operations. That is why they consider the following steps when building an efficient manufacturing cybersecurity program:
- Perform a cybersecurity maturity assessment
- Prioritize actions based on risk profiles
- Establish a formal governance program with IoT
The threat landscape in IoT compels you to install systems that control the operations of your production facility, proliferating rapidly with the increase in digitalization and advanced technologies such as IoT.
Boosting visibility and traceability in smart factories through laser scanners
The laser-scanning technology is beneficial in identifying manufacturing objects. For instance, Radio Frequency Identification Devices or RFIDs are used for converting various resources into Smart Manufacturing Objects or SMOs.
By using a laser scanner on the shop floors, you can enable the real-time display of the movements of the SMOs and see where you are at when it comes to manufacturing processes.
You can assess the production lines and industrial activities with the visual records of every shift and assembly stage. The technology helps you in improving the output and ensuring high-end products.
Technology usage for Smart Manufacturing enablement
Smart Manufacturing does not require 5G, but it needs support that reduces hardware reliance and simplifies setups, offering greater bandwidth than 5G.
That is where cellular IoT and LoRaWAN enter the picture, for they can piggyback on AI to send alerts or make process decisions independently.
Cellular IoT, for instance, connects physical objects such as IoT sensors to the internet using the same network as smartphones. It is responsible for securing your iPhone to Google Maps, email service providers, and Instagram. Cellular IoT carries your voice through the air.
On the other hand, LoRaWAN is a network protocol using the point-to-multipoint approach. It is responsible for identification and encryption and includes a cloud component that the multiple gateways can connect to.
Over to you
As internet-enabled devices continue gaining precedence in the manufacturing sector, it is essential to note that businesses will benefit from IoT technology immensely if implemented correctly.
From cost savings and production efficiency to worker safety and emergency preparedness, there is not one aspect in manufacturing that is not affected by IoT. Are you ready to leverage IoT for your business?